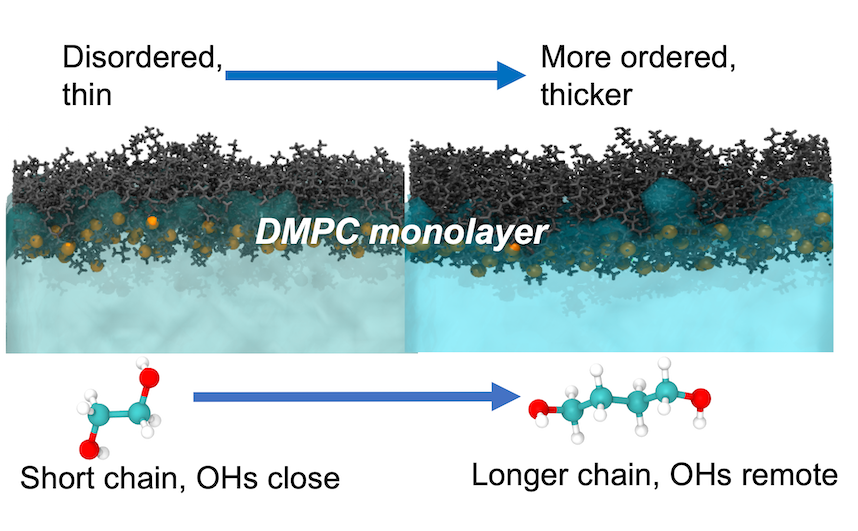
The effect that solvents and co-solvents have on the structural and dynamic properties of lipid molecules in self-assembled structures is of significant interest for a variety of applications ranging from drug delivery and personal care formulations to cryopreservation. In this manuscript, we elucidate the underlying molecular scale mechanisms which lead to the different effects that various diols, with varying carbon chain lengths and patterns of hydroxylation, have on the structural and interfacial properties of a DMPC (1,2-dimyristoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine) monolayer. Specifically, we have investigated the behaviour of DMPC monolayers interacting with pure solvents containing 1,2-ethanediol, 1,2-propanediol, 1,3-propanediol, 1,2-butanediol, 1,3-butanediol and 1,4-butanediol, as well as water. While the structure of phosphocholine membranes have been studied with aqueous solutions containing diols as a solvent, there has been little to no work done investigating the properties of lipid membranes interacting with pure diol solvents. In this work, we have used all-atom molecular dynamics simulations to characterise the structural and interfacial properties of the monolayers in contact with each of these pure diol solvents, and obtain a detailed understanding of how the chemical structure of the diols plays a key role in the effects that each has on the lipid monolayer.
The results of our work shows that, in comparison to water, all of the diols studied result in a more disordered and thinner monolayer. We find that the shorter diols with the hydroxyl groups on neighbouring carbons (1,2-ethanediol and 1,2-propanediol) are able to penetrate deeper into the head group region of the lipid monolayers and as a result significantly disorder and thin the monolayers. Like water, we find that the diols also form hydrogen-bonded networks that connect the DMPC head groups in neighbouring molecules. Interestingly, we find that the distribution of the hydroxyl groups within the diol molecules has a significant effect on the solvent-mediated interactions between the DMPC head groups. The results presented in this manuscript could be quite important in the future design of pharmaceutical and personal care formulations.
Full reference: On the interactions of diols and DMPC monolayers. Nastasha H. Rhys, David J. Barlow, M. Jayne Lawrence & Christian D. Lorenz, Journal of Molecular Liquids (2022) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2022.119963.