In this manuscript, we present important findings of how lipid heterogeneity in model lipid membranes affect various structural and dynamic properties of the lipids within the membranes . We report the results of large-scale all-atom molecular dynamics simulations of commonly used simple model lipid membranes as well as two complex models of the lipid membranes, consistent with the lipid profile reported to have been found in healthy cells and those from patients with Alzheimer’s disease by Chen et al, J. Biol. Chem. (2012) 287, 2678-2688.
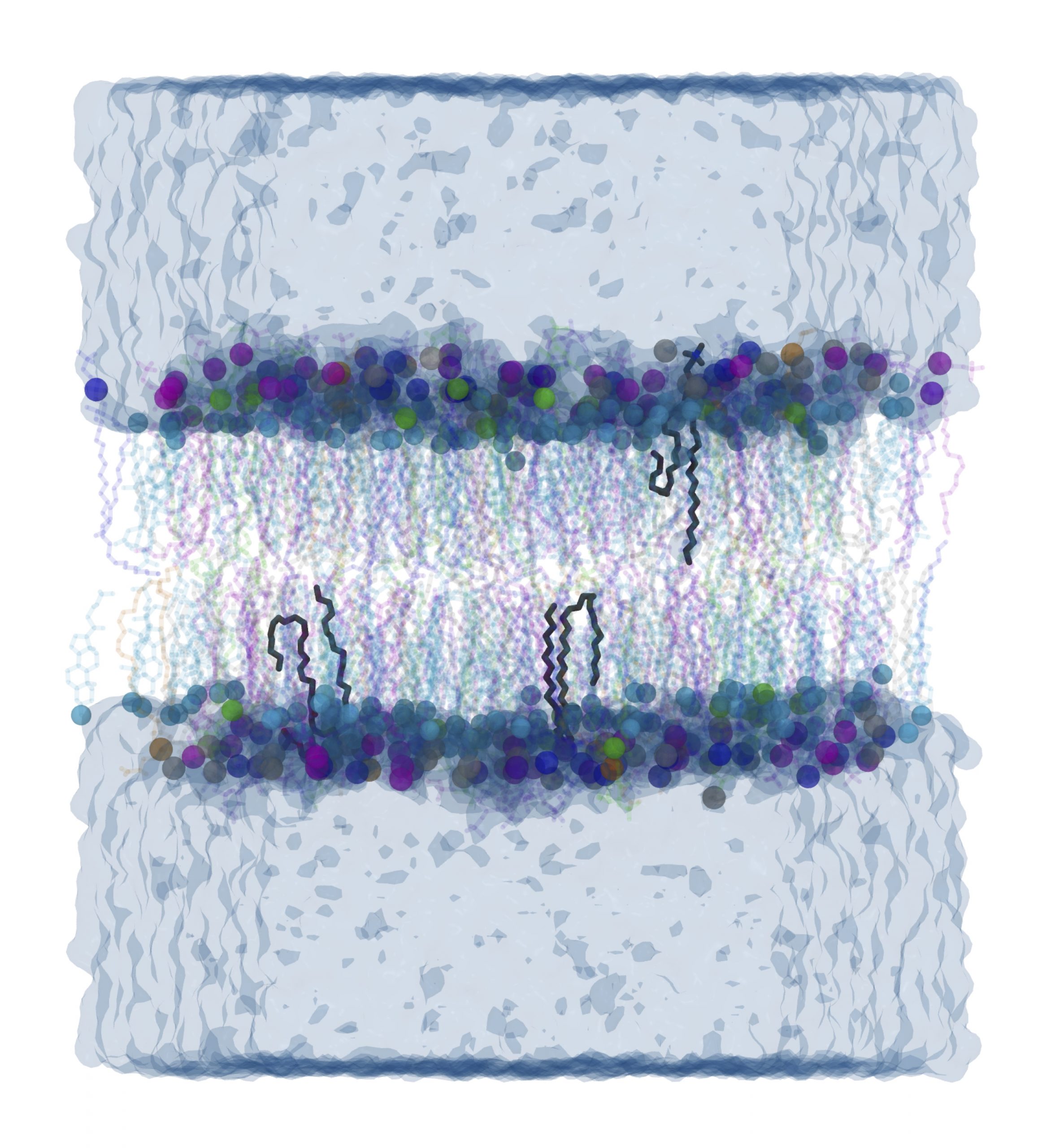
By comparing various physical and dynamic properties of the membranes, we found that there are several differences, with the most significant being in the measures of the dipole potential and diffusion coefficients of the lipids within the membranes. The differences in these two quantities are explained in terms of the different lipid types which make up the various membranes investigated. The differences observed could have a significant impact when using simulations to assess other properties such as the permeability of small molecules across model membranes. Additionally, we have observed the interesting phenomena of the lipid tail’s ‘snorkelling’ toward the lipid water interface in both membranes. We found that this snorkelling behaviour is more prevalent as the unsaturation of the lipid tails increases and also as the lipid tail lengths increases. To our knowledge, this is the first time such a phenomenon has been reported for lipid tails themselves, which would have significant implication in understanding a wide range of processes within the complex biological membranes found in cells. In addition to providing insight into how lipid heterogeneity affects the various properties measured, we also provide a detailed description of various properties of the healthy and diseased lipid membranes presented in this manuscript, which will be of interest to those scientists working on developing new therapeutic strategies for the prevention and treatment of Alzheimer’s and potentially other neurological diseases.
Full reference: “Effect of lipid heterogeneity on model human brain lipid membranes“, Sze Yee, Richard Gillams, Sylvia Ellen McLain & Christian D. Lorenz, Soft Matter (2021) 17, 126-135.