Auxiliary Metamodel
This pattern is one of the fundamental
MT design patterns.
Summary
The pattern consists of the
introduction of a metamodel
for auxiliary data or operations,
neither part of the source or target
language, to support the processing
of a model transformation.
Application conditions
Signs that this pattern is necessary
include: (i) excessively complex
expressions are read within rules; (ii) duplicated
expressions occur across different rules;
(iii) complex ad-hoc data structures
are used within the transformation;
(iv) tracing or other
information is needed during the
transformation execution in order to
control the transformation processing.
Solution
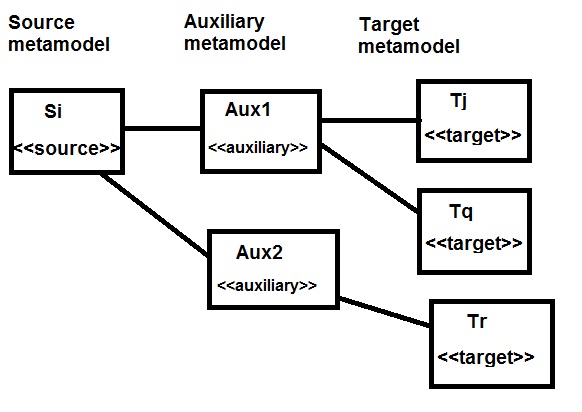
Define the auxiliary metamodel
as a set of (meta) attributes, associations, entity types, operations and
generalisations additional to
the source and/or target
metamodels. The auxiliary data
may be constructed by some rules
(eg., the construction of explicit trace
objects) and read by other rules.
Benefits
This pattern helps to simplify the complexity of model
navigations and constructions in a transformation, and to
decompose the transformation
into subparts/phases.
Complex relationships
between a source and target model can be decomposed
into simpler relationships between these models and
an intermediate model using the auxiliary metamodel. It can be used to store
information about the transformation
execution, to support optimisations or
change-propagation.
Disadvantages
The auxiliary data must be managed and
kept up-to-date.
Applications and examples
This pattern is applicable to all
categories of transformations. It is a
strong candidate for inclusion as an
in-built facility in model transformation
languages,
because of its wide applicability.
In Triple Graph Grammars (TGG),
correspondence graphs can be defined using auxiliary classes and
associations. These record
detailed traces to assist in the
control of the transformation.
Auxiliary Metamodel would be
applicable to examples such as the
complex tuple structures used
in the ATL solution to the class diagram
to relational database problem
SimpleClass2SimpleRDBMS.
Auxiliary Metamodel can be used to add artificial
structure to a model, such as a root element, to
assist in navigation. It can be used to
store transformation parameter data,
to enable parameterisation of a
transformation.
It can also be used to precompute
expression values prior to a transformation execution,
to avoid duplicated evaluations, or to
simulate multiple element matching in
rules by single element matching.
Auxiliary metamodels are also used to implement explicit
tracing facilities. In transformation languages such
as Viatra and Kermeta,
the auxiliary entities and associations record information
such as a history of rules applied and connections
between target model elements and the source model
elements they were derived from.
Related patterns
This pattern is used by
Auxiliary Correspondence Model,
Simulate Multiple Matching and
Simulate Collection Matching.
The classic programming technique of
memoisation also
introduces auxiliary data structures in
order to avoid redundant computations.
The pattern can evolve to the Auxiliary Models
pattern
if separate models of auxiliary or
intermediate data are required to carry
out the transformation.

